Installation of Oracle Database 11g Release 2 (11.2) On Fedora 14 (F14)
Download Software
Download the following software.
Unpack Files
Unzip the files.
unzip linux.x64_11gR2_database_1of2.zip unzip linux.x64_11gR2_database_2of2.zip
You should now have a single directory called "database" containing installation files.
Hosts File
The "/etc/hosts" file must contain a fully qualified name for the server.
<IP-address> <fully-qualified-machine-name> <machine-name>
Set Kernel Parameters
Oracle recommend the following minimum parameter settings.
Add or amend the following lines in the "/etc/sysctl.conf" file.
Open /etc/sysctl.conf and add the following lines without any linespace.
fs.aio-max-nr = 1048576 fs.file-max = 6815744 kernel.shmall = 2097152 kernel.shmmax = 536870912 kernel.shmmni = 4096 kernel.sem = 250 32000 100 128 net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 9000 65500 net.core.rmem_default = 262144 net.core.rmem_max = 4194304 net.core.wmem_default = 262144 net.core.wmem_max = 1048586
Run the following command to change the current kernel parameters.
/sbin/sysctl -p
Add the following lines to the "/etc/security/limits.conf" file without any linespace.
oracle soft nproc 2047 oracle hard nproc 16384 oracle soft nofile 1024 oracle hard nofile 65536
Add the following line to the "/etc/pam.d/login" file, if it does not already exist.
Start the Firewall administration dialog (System > Administration > Firewall). Click the "Disable" button followed by the apply button on the toolbar, then close the dialog.
session required pam_limits.so
Start the Firewall administration dialog (System > Administration > Firewall). Click the "Disable" button followed by the apply button on the toolbar, then close the dialog.
Disable secure linux by editing the "/etc/selinux/config" file, making sure the SELINUX flag is set as follows.
Alternatively, this alteration can be done using the GUI tool (Applications > System Settings > Security Level). Click on the SELinux tab and disable the feature. If SELinux is disabled after installation, the server will need a reboot for the change to take effect.SELINUX=disabled
Restart your system.
Setup
If you have installed the suggested package groups during the installation, the majority of the necessary packages will already be installed. The following packages are listed as required, including the 32-bit version of some of the packages.
[root@localhost oracle]# yum install binutils
Loaded plugins: langpacks, presto, refresh-packagekit
Adding en_US to language list
Error: Cannot retrieve repository metadata (repomd.xml) for repository: fedora. Please verify its path and try again
Solution
It turned out that my local DNS server was the problem so I stopped it and added in /etc/hosts these 2 lines:
If gives error such as
[root@localhost oracle]# yum install binutils
Loaded plugins: langpacks, presto, refresh-packagekit
Adding en_US to language list
Error: Cannot retrieve repository metadata (repomd.xml) for repository: fedora. Please verify its path and try again
Solution
It turned out that my local DNS server was the problem so I stopped it and added in /etc/hosts these 2 lines:
Code:
80.239.156.215 mirrors.fedoraproject.org 213.129.242.84 mirrors.rpmfusion.org
yum install binutils yum install compat-libstdc++-33 yum install compat-libstdc++-33.i686 yum install elfutils-libelf yum install elfutils-libelf-devel yum install gcc yum install gcc-c++ yum install glibc yum install glibc.i686 yum install glibc-common yum install glibc-devel yum install glibc-devel.i686 yum install glibc-headers yum install ksh yum install libaio yum install libaio.i686 yum install libaio-devel yum install libaio-devel.i686 yum install libgcc yum install libgcc.i686 yum install libstdc++ yum install libstdc++.i686 yum install libstdc++-devel yum install make yum install numactl-devel yum install sysstat yum install unixODBC yum install unixODBC.i686 yum install unixODBC-devel yum install unixODBC-devel.i686
Create the new groups and users.
groupadd oinstall groupadd dba groupadd oper groupadd asmadmin useradd -g oinstall -G dba,oper,asmadmin oracle passwd oracle
Note. We are not going to use the "asmadmin" group, since this installation will not use ASM.
Create the directories in which the Oracle software will be installed.
mkdir -p /u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0/db_1 chown -R oracle:oinstall /u01 chmod -R 775 /u01
Login as root and issue the following command.
xhost +<machine-name>
Edit the "/etc/redhat-release" file replacing the current release information "Fedora release 14 (Laughlin)" with the following.
Login as the oracle user and add the following lines at the end of the ~/.bash_profile file.redhat release 5
# Oracle Settings
TMP=/tmp; export TMP
TMPDIR=$TMP; export TMPDIR
ORACLE_HOSTNAME=localhost.localdomain; export ORACLE_HOSTNAME
ORACLE_UNQNAME=orcl; export ORACLE_UNQNAME
ORACLE_BASE=/u01/app/oracle; export ORACLE_BASE
ORACLE_HOME=$ORACLE_BASE/product/11.2.0/db_1; export ORACLE_HOME
ORACLE_SID=orcl; export ORACLE_SID
ORACLE_TERM=xterm; export ORACLE_TERM
PATH=/usr/sbin:$PATH; export PATH
PATH=$ORACLE_HOME/bin:$PATH; export PATH
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$ORACLE_HOME/lib:/lib:/usr/lib; export LD_LIBRARY_PATH
CLASSPATH=$ORACLE_HOME/JRE:$ORACLE_HOME/jlib:$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/jlib; export CLASSPATH
if [ $USER = "oracle" ]; then
if [ $SHELL = "/bin/ksh" ]; then
ulimit -p 16384
ulimit -n 65536
else
ulimit -u 16384 -n 65536
fi
fi
Installation
Log into the oracle user. If you are using X emulation then set the DISPLAY environmental variable.
Restart your computer.DISPLAY=<machine-name>:0.0; export DISPLAY
Start the Oracle Universal Installer (OUI) by issuing the following command in the database directory.
[oracle@localhost ~]$ cd database/ ./runInstaller
The OUI (Oracle Universal Installer) should start and you should see following screens in the order given below:1. Provide your email address and Oracle support password to get security updates from Oracle.2. Installation options like creating a database, installing oracle software only or upgrading the database. Select "Create and configure a database".3. Choose the system class here. Select "Server Class" it provides more advanced options.4. Choose from creating a single node installation or RAC.5. Choose your installation Typical or Advanced. We will go with typical at this moment.6. If you choose typical install in previous screen, then you will see this page for Install Configurations. Provide Oracle software installation location, database files location and administrator password etc.7. Specify the Oracle install inventory location and Operating system group "oinstall".8. Now all prerequisite checks will be performed here and if every thing is ok you will be moved to the install summary page. You can hit the "Back" button and come back to see the status of all the checks performed.
9. Installation Summary page. Hit "Finish" to start the Installation.
10. Installation Progress. This will take several minutes and it will automatically invoke Database COnfiguration Assistant to create a database.
11. Database Configuration Assistant invoked by the installer.
12. Once DBCA has finished creating the database, it will show a page like this. It is a summary of the database that has just been created.
13. As a last step you will be asked to execute some configuration scripts as root.
Post Installation
Edit the "/etc/redhat-release" file restoring the original release information.
Fedora release 14 (Laughlin)
Edit the "/etc/oratab" file setting the restart flag for each instance to 'Y'.
orcl:/u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0/db_1:Y
What is needed to connect PUTTY to Fedora 14 ?
Make sure the sshd service is enabled and started.
Code:
su -c 'chkconfig sshd on'
su -c 'service sshd restart'
I have solved by disabling Firewall and then apply. The other long way is under:
Well Problem Solved! I searched around on the forums and found a thread that helped me out.
http://forums.fedoraforum.org/showth...re+list+server
Explained what I needed to do to configure my machine
It turns out that I needed to install the samba client. I installed the packages
su root
yum install samba-client.i686 samba-common.i686
Then, I had to install
system-config-samba
I ran
system-config-samba
and it seemed to start up fine. This config file seems to be geared towards the windows platforms accessing shares from your linux box. I didn't configure anything here. The thread then says to modify your firewall.
I then ran
system-config-firewall
and enabled samba in the "trusted services". It was able to access my windows network shares after that.
I did the configurations through the gui of each of the config files, but if anyone has a spare second, I'd love to learn how to configure the settings from within the terminal itself. Or a link to a thread explaining the commands in terminal would be great!
Note:change the below lines of above ~/.bash_profile file by reopening in vi or other editor.ORACLE_HOSTNAME = ora11g.home.com with your own host name andORACLE_SID=ora11g with your own SID name which you have entered at the time of oracle installation
Automating Database Startup and Shutdown on Linux
The following represents the Oracle recommended method for automating database startup and shutdown of Oracle 9i instances on Linux, but it works equally well for Oracle 10g, 11G and 12c also. It can be used on any RHEL-style distribution, including Oracle Linux, up to an including RHEL6.
Once the instance is created, edit the "/etc/oratab" file setting the restart flag for each instance to 'Y'.
orcl:/u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0/db_1:Y
Next, create a file called "/etc/init.d/dbora" as the root user, containing the following.
This method can still be used under Oracle 10g, 11g and 12c, provided the "ORA_HOME" variable is amended to use the correct path and this is added to the end of the
dbstart and dbshut lines. The lines to start and stop the listener can be removed under Oracle 10g Release 2 onward, as the dbstart command includes an automatic start of the listener.#!/bin/sh # chkconfig: 345 99 10 # description: Oracle auto start-stop script. # # Set ORA_HOME to be equivalent to the $ORACLE_HOME # from which you wish to execute dbstart and dbshut; # # Set ORA_OWNER to the user id of the owner of the # Oracle database in ORA_HOME. #ORA_HOME=/u01/app/oracle/product/10.2.0/db_1 #ORA_HOME=/u01/app/oracle/product/11.1.0/db_1
ORA_HOME=/u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0/db_1
#ORA_HOME=/u01/app/oracle/product/12.1.0/db_1
ORA_OWNER=oracle
export ORACLE_UNQNAME=orcle
if [ ! -f $ORA_HOME/bin/dbstart ]
then
echo "Oracle startup: cannot start"
exit
fi
case "$1" in
'start')
# Start the Oracle databases:
# The following command assumes that the oracle login
# will not prompt the user for any values
su $ORA_OWNER -c "$ORA_HOME/bin/dbstart $ORA_HOME"
touch /var/lock/subsys/dbora
;;
'stop')
# Stop the Oracle databases:
# The following command assumes that the oracle login
# will not prompt the user for any values
su $ORA_OWNER -c "$ORA_HOME/bin/dbshut $ORA_HOME"
rm -f /var/lock/subsys/dbora
;;
esac
Use the
chmod command to set the privileges to 750.chmod 750 /etc/init.d/dbora
Associate the dbora service with the appropriate run levels and set it to auto-start using the following command.
chkconfig --add dbora
Create symbolic links to the
dbora script in the appropriate run-level script directories as follows.# ln -s /etc/init.d/dbora /etc/rc.d/rc0.d/K01dbora
# ln -s /etc/init.d/dbora /etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S99dbora# ln -s /etc/init.d/dbora /etc/rc.d/rc5.d/S99dboraNext, we must create the "startup.sh" and "shutdown.sh" scripts in the "/home/oracle/scripts". First create the directory.# mkdir -p /home/oracle/scripts # chown oracle.oinstall /home/oracle/scripts
The "/home/oracle/scripts/startup.sh" script should contain the following commands.
#!/bin/bash
export TMP=/tmp
export TMPDIR=$TMP export ORACLE_BASE=/u01/app/oracle
export ORACLE_HOSTNAME=localhost.localdomain
export ORACLE_UNQNAME=orcl
export ORACLE_HOME=$ORACLE_BASE/product/11.2.0/db_1
#export ORACLE_HOSTNAME=ol6-121.localdomain #export ORACLE_UNQNAME=db12c #export ORACLE_HOME=$ORACLE_BASE/product/12.1.0/db_1 export PATH=/usr/sbin:$ORACLE_HOME/bin:$PATH export ORACLE_SID=db12c ORAENV_ASK=NO . oraenv ORAENV_ASK=YES # Start Listener lsnrctl start # Start Database sqlplus / as sysdba << EOF STARTUP; EXIT; EOF
The "/home/oracle/scripts/shutdown.sh" script is similar.
#!/bin/bash export TMP=/tmp export TMPDIR=$TMP export ORACLE_BASE=/u01/app/oracle
export ORACLE_UNQNAME=orcl
export ORACLE_HOSTNAME=localhost.localdomain
export ORACLE_HOME=$ORACLE_BASE/product/11.2.0/db_1 #export ORACLE_HOSTNAME=ol6-121.localdomain #export ORACLE_UNQNAME=db12c #export ORACLE_HOME=$ORACLE_BASE/product/12.1.0/db_1 export PATH=/usr/sbin:$ORACLE_HOME/bin:$PATH export ORACLE_SID=db12c ORAENV_ASK=NO . oraenv ORAENV_ASK=YES # Stop Database sqlplus / as sysdba << EOF SHUTDOWN IMMEDIATE; EXIT; EOF # Stop Listener lsnrctl stop
Note. You could move the environment settings into the "dbora" file or into a separate file that is sourced in the startup and shutdown script. I kept it local to the script so you could see the type of things that need to be set in case you have to write a script to deal with multiple installations, instances and listeners.
Make sure the permissions and ownership of the files is correct.
# chmod u+x /home/oracle/scripts/startup.sh /home/oracle/scripts/shutdown.sh # chown oracle.oinstall /home/oracle/scripts/startup.sh /home/oracle/scripts/shutdown.sh
Restart your system and you will see the listener and database will now start and stop automatically with the machine. You may test as follows:
oracle@192.168.1.200's password:
Last login: Wed Feb 6 05:10:13 2013 from 192.168.1.141
[oracle@localhost ~]$ sqlplus
SQL*Plus: Release 11.2.0.1.0 Production on Wed Feb 6 05:24:31 2013
Copyright (c) 1982, 2009, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Enter user-name: sys/syspassward@databasename as sysdba
Connected to:
Oracle Database 11g Enterprise Edition Release 11.2.0.1.0 - Production
With the Partitioning, OLAP, Data Mining and Real Application Testing options
SQL> grant connect,resource,dba to username identified by passward;
In Oracle 11g a new parameter called SEC_CASE_SENSITIVE_LOGON which is defaults to TRUE for case sensitive passwords. My SCOTT password was "tiger" is small case and Forms 10g was taking it as "TIGER" on runtime. Solution 1: - Connect as sys and change the parameter to false.
alter system set SEC_CASE_SENSITIVE_LOGON = FALSE;
Otherwise following error will occured.
ORA-01017 Invalid username/password logon denied
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E11882_01/backup.112/e10642/rcmdupdb.htm
http://www.oracle-base.com/articles/11g/duplicate-database-using-rman-11gr2.php
http://gemsofprogramming.wordpress.com/2013/03/18/duplicate-a-11gr2-database-with-rman-the-one-where-we-duplicate-from-a-backup/
http://www.dbspecialists.com/blog/database-backups/duplicating-an-11gr2-oracle-database-with-no-connection-to-the-target/
If you would like to do a basic smoketest of the installed database software to confirm the installation was successful, try doing the following:
If you have got this far with your installation of Oracle 11g, all is well. The core Oracle 11g database software is installed and working. You may have some tweaking to do for your particular requirements but that is outside the scope of this post.
As part of the database installation a sample HR schema was installed but left locked. Here is how to unlock this sample schema using sqlplus:
At this stage you should be able to invoke the Oracle sqldeveloper GUI by invoking $ORACLE_HOME/sqldeveloper/sqldeveloper/bin/sqldeveloper. However before you can log in, you have to configure a valid connection. As an example of how to configure a valid connection, here is my HR connection properties:
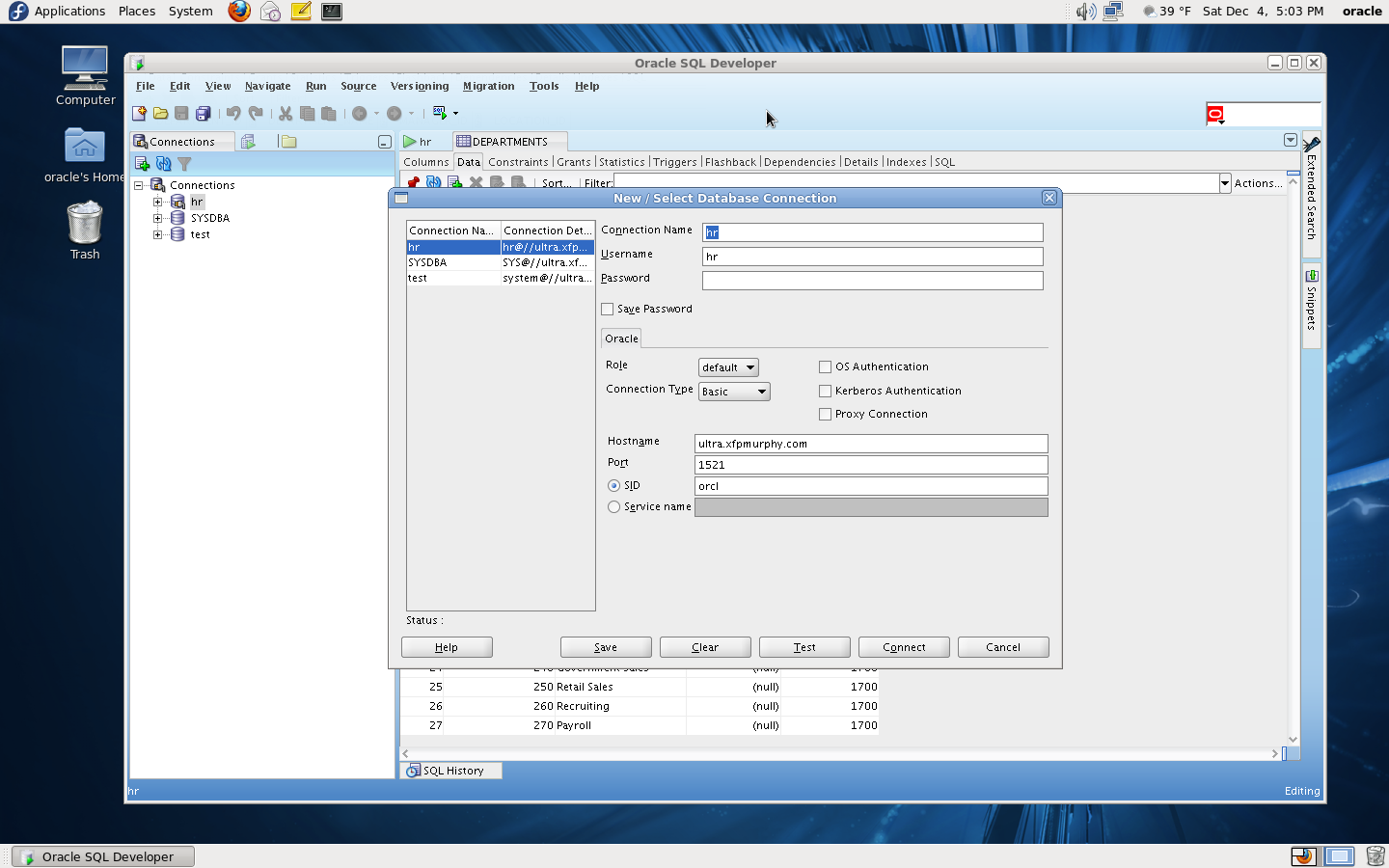
Once you have configured a valid connection, you will be able to login as user HR and examine the HR schema.

To automatically start and stop the Oracle database during system startup and shutdown you need to place an appropriate script in the /etc/rc.d/init.d directory and symbolically link it to the appropriate rc directories. See this post for an example of such a script.
An Oracle Instant Client gives customers the ability to quickly install and deploy Oracle applications including sqlplus on various platforms including Microsoft Window 7 without installing the standard Oracle client or having an ORACLE_HOME. Instant Clients for 32-bit Microsoft Windows are available here . You need to download two packagee, i.e the Instant Client Package – Basic Lite (contains English error messages and Unicode, ASCII, and Western European character set support) and the Instant Client Package – SQL*Plus (contains additional libraries and executable for running SQL*Plus with Instant Client.)
Unzip the two packages into a single directory such as C:\SQLPLUS. Then edit the configuration file tnsnames.ora which you will find in this directory to configure the connection to your Fedora 14 system.
If you are using a firewall on your Fedora 14 platform (which you should be!), you will have to modify iptables to open port 1521 for TCP packet send and receive. Here are the appropriate lines to add to /etc/sysconfig/iptables:
In a production environment these rules should be modified to restrict the range of IP addresses that can access the 1521 port.
Once you have configured a valid connection, you will be able to connect to the Oracle database from your Windows 7 platform.
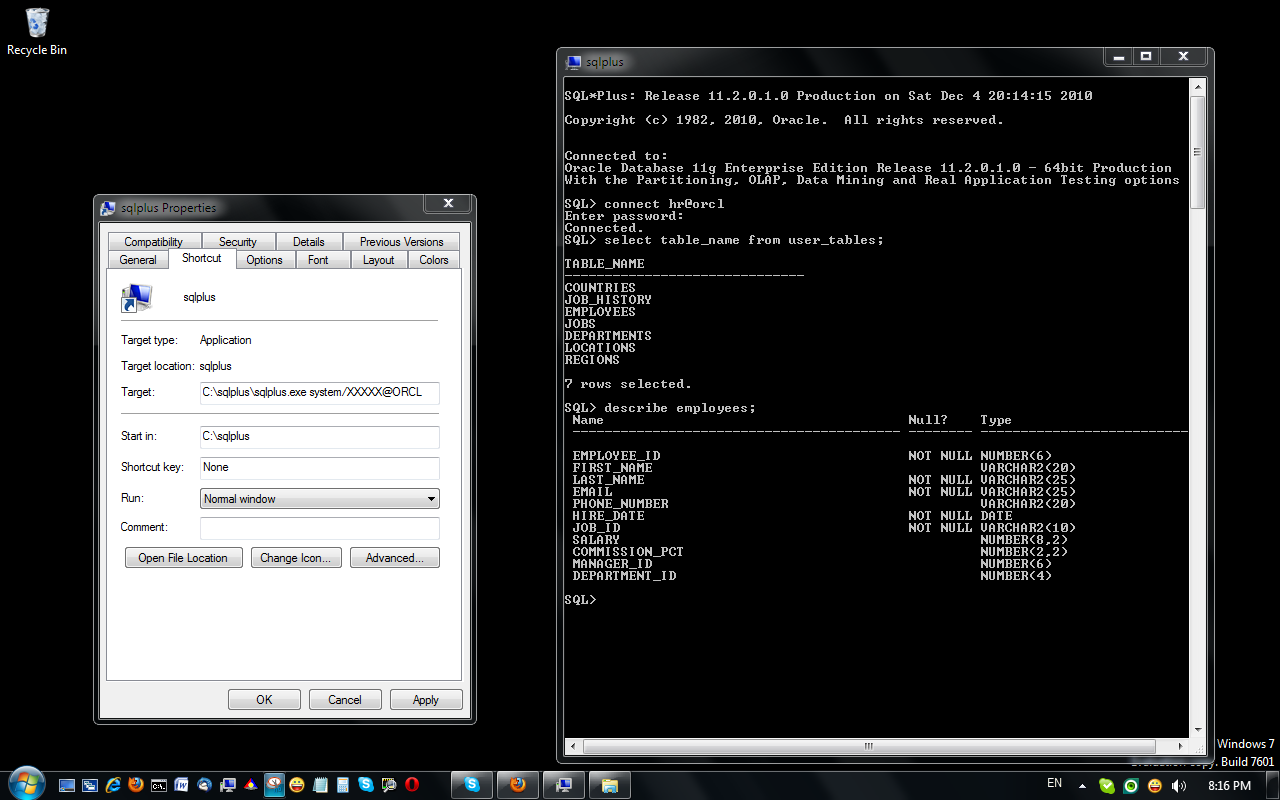
If security is not an issue, you can add a shortcut as shown above so that you are automatically connected to a schema.

If security is not an issue, you can add a shortcut as shown above so that you are automatically connected to a schema.
Well, time to stop. The information in this post should be enough to get you up and running. Please let me know if I left out anything important that you feel would of been of help to you in installing Oracle 11g on Fedora 14 and I will add it to this post.















No comments:
Post a Comment